
Whether you are –
A pregnant lady
A growing kid
An old person
A fitness buff
Omega 3 offers monumental benefits to everyone.
Studies by the nutrition community have revealed the amazing benefits of omega 3. Its plays a vital role in improving our health and fitness. It is one of the most studied and researched nutrients on the planet.
This incredible nutrient comes with one caveat, though.
Your body cannot make omega 3, on its own. It is your responsibility to provide it to your body through the diet.
That’s why it falls under the category of essential fatty acid.
Note:
In this omega 3 guide, I have tried to answer the maximum number of questions about omega 3 and fish oil supplements.
Apart from the benefits of omega 3, you will get answers to the questions like
- What is omega 3?
- How much you need in a day?
- Side effects of omega 3 and fish oil?
- The best time to take omega 3 supplements?
- How to choose a good supplement brand of fish oil?
- What are the good supplement brands?
Before we start with the benefits of omega 3 you should know
There are three types of omega 3 fatty acids:
ALA – Alpha-Linolenic Acid
EPA – Eicosapentaenoic Acid
DHA – Docosahexaenoic Acid
We will discuss them later.
Table of Contents
The 10 important health benefits of omega 3
1. Omega 3 benefits the 100 billion brain cells of your brain
A fatty body is unhealthy, but a fatty brain is bright and brilliant.
The brain is the fattiest organ made up of 60% fat. Also, it carries more than 100 billion cells, and omega 3 fatty acids form the building blocks of these cells.
The brain has a very high concentration of omega 3 and 90% of this omega 3 is in the form of DHA.
It plays a significant role in building healthy cell membranes, forming important brain chemicals, and improving nerve transmission.
DHA forms an integral part in the structure of the cerebral cortex. The cerebral cortex is responsible for memory, language, creativity, emotion, and attention.
2. Omega 3 can prevent many crippling eye disorders
The retina contains a high concentration of omega 3 fatty acid (DHA). It helps in maintaining the integrity and structure of the retina.
Many eye doctors recommend a good quality omega 3 to reduce the risk of eye problems.
Omega 3 has also shown to reduce and prevent many eye disorders like –
Macular degeneration – The omega-3 have shown to reduce the risk of macular degeneration (MD), a crippling eye disorder that’s one of the biggest causes of blindness globally.
Diabetic Retinopathy – It’s a condition that damages the blood vessels in the eyes. Diets high in omega 3, can lower these damages.
Glaucoma – A condition of increased pressure within the eyes. Omega 3 helps in adjusting the blood flow in the eye to relieve this pressure.
Dry eye caused by wearing contact lenses – Excessive or improper use of lenses can cause dry eye. DHA can repair these nerves and decrease eye dryness.
3. Omega 3 makes you fall asleep quickly
What happens when you can’t sleep properly in the night? The next day you feel lethargic, unmotivated, and irritated.
Everyone knows the importance of a good night’s sleep. It repairs and refreshes the brain and body on so many levels. Omega 3 has been shown to improve the quality of sleep and helps you fall asleep quickly. More the omega 3 concentration in the blood, less the sleep-related problems you will have.
DHA boosts melatonin levels. Melatonin, also known as the sleep hormone, controls our sleep and wake cycles.
Studies have shown that low levels of DHA can cause melatonin deficiency – and an increase in DHA causes the melatonin levels to rise.
4. Omega 3 reduces inflammation by activating the antioxidant pathways
Omega 3 helps in reducing inflammation in two ways:
1. By providing Resolvins
Omega 3 fatty acids are one of the best ways to counter inflammation because they provide your body with chemicals called resolvins.
This remarkable substance turns off inflammation in the body when it is no longer needed to fight infection.
2. By turning on the pathway of Nrf2
Nrf2 (Nuclear factor erythroid 2) is a special protein which lies dormant in every cell. When the inflammation due to oxidative stress increases, an alarm in the body will turn on the Nrf2 pathway.
The Nrf2 protein then bonds with DNA in the cell. And this bonding opens the door for a vast array of important antioxidants as well as detoxification enzymes.
This pathway reduces inflammation and eliminates harmful toxins from the body. Omega 3 helps in activating this pathway.
5. Omega 3 helps in creating new bone cells
Like muscles, bones are active tissue. New bone tissues are forming while removing the old and broken tissues.
These processes are known as:
osteoblast – formation of new bone cells
osteoclast – break down of bone cells
Creating new bone cells takes longer than breaking down old cells.
When the inflammation in the body is higher, the osteoclast activity increases. If inflammation remains elevated, it can lead to a decrease in bone density, which can advance to osteoporosis.
Omega 3 reduces inflammation, which will dial down the osteoclast activity. Thus, destroying fewer bone cells.
In addition to reducing the inflammation, omega 3 also promotes osteoblast activity. This process will give bones enough time to make new bone cells, increasing the bone density.
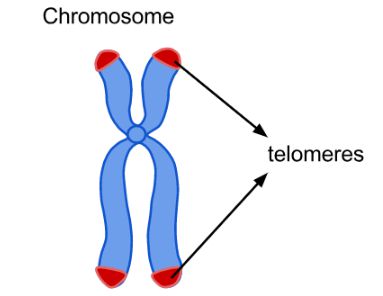
6. Omega 3 can slow down the ageing process by increasing the length of Telomeres
Telomeres hold secrets to our health and how we age. Telomeres are the caps on the ends of the chromosomes. The length of these telomeres affects the ageing of our cells.
Longer telomeres mean slower ageing, and shorter telomeres mean faster ageing. Studies have shown that omega 3 (especially DHA) increases the activity of telomerase enzyme which lengthens telomeres.
7. It can reduce the risk of heart diseases
High levels of triglyceride in the blood are associated with an increased risk of heart diseases. Increasing the amount of omega 3 in your diet will reduce your triglyceride levels, without affecting LDL and HDL cholesterol.
8. Omega 3 can help in bodybuilding
The research is out, and the finding is clear – omega 3 promotes muscle gain. And the icing on the top, it also prevents muscle loss.
Omega 3 increases the process of MPS (Muscle Protein Synthesis). In other words, it enhances the uptake of protein to the muscles resulting in higher muscle growth.
A 2012 study revealed that the women taking omega 3 fish oil (2000mg of EPA/DHA) every day along with daily exercise, saw an improvement in their muscle strength. This finding was in comparison to the women doing regular exercise without taking omega 3 fish oil.
9. Omega 3 can reduce muscle soreness
The soreness you feel the next day after a strenuous workout can affect the performance of your next workout session.
Omega 3, with its anti-inflammatory effect, lowers the muscle soreness and speeds up the muscle recovery. This dual effect results in better exercise sessions with lesser soreness.
10. Omega 3 is beneficial in speeding up your fat loss
Although you cannot think of omega 3 as a fat burner, you can feel its effect on your body fat.
A 2015 meta-analysis of omega 3’s effect on weight loss proved no clear evidence of omega 3 actively helping in weight loss. But the research showed a significant reduction in abdominal fat.
This means that if you are on a fat loss diet adding omega 3 fish oil will boost your fat loss process.
All these benefits of omega 3 will convince you to incorporate it into your diet. But, apart from knowing the importance of omega 3 for our health, people get scant information regarding omega 3.
This lack of knowledge leaves people with lots of unanswered questions. They feel clueless about how to add optimum quality and quantity of omega 3 in the diet.
The following questions will answer all your curious doubts on omega 3.
What is omega 3?
Omega 3 is short for Omega 3 Fatty Acids. They fall under the category of essential fatty acids because your body cannot produce omega 3 by itself. You have to provide it through food sources.
Chemistry Alert:
Omega 3 is a family of essential polyunsaturated fatty acids which contain a chain of carbon atoms linked by chemical bonds. They have two ends, one end has a methyl group, and the other end has a carboxyl group. The term Omega refers to the methyl end.
Polyunsaturated means that it contains more than one double bond. The first double bond appears at the third carbon position from the methyl end hence the name omega 3.
Omega 3s are vital for the body because it has many important metabolic functions in the body like, maintaining the integrity of the cell membrane and regulating the body’s immunity system. They also help in the exchange of nutrients and the elimination of waste within a cell.
Types of Omega 3
Omega 3 is a family of 11 different types of fatty acids.
The three main types of omega 3 fatty acids are
ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid) – It’s a chain of 18 carbons, with 3 double bonds. They are mainly found in plant sources. Our body cannot use ALA directly. It has to first convert the ALA to EPA and DHA to use it.
This conversion process is very inefficient. 1-10% of ALA converts to EPA, and 0.5-5% converts to DHA.
Natural Sources of ALA – Brussels sprouts, Seaweed, Chia seed, Flaxseed, Hemp seed, Walnuts, Spinach, Broccoli
EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid) – It is 20 carbon long, with 5 double bonds.
The primary function of EPA is to form eicosanoids – the signalling molecules. Eicosanoids have vital physiological functions like reducing inflammation.
DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid) – It has a chain of 22 carbons, with 6 double bonds. It is an integral structural component of the retina and skin. It is vital for the development and proper functioning of the brain.
Natural Sources Of EPA And DHA – Free-range Eggs, Fatty Fish like sardines, salmon, mackerel, shrimps, etc.
Other types of omega 3
8 other types of omega 3 fatty acids are discovered so far. But these are not considered essential.
- Hexadecatrienoic acid (HTA)
- Eicosatetraenoic acid (ETA)
- Eicosatrienoic acid (ETE)
- Stearidonic acid (SDA)
- Heneicosapentaenoic acid (HPA)
- Docosapentaenoic acid (DPA)
- Tetracosapentaenoic acid
- Tetracosahexaenoic acid
Is omega 3 good for the heart?
The studies conducted using sea-food as the source of omega 3 showed a positive correlation between eating fish and a reduction in the risk of heart diseases.
Inflammation can damage blood vessels which can lead to heart diseases. Since omega 3 reduces inflammation throughout the body, it can aid in preventing the cause of heart disease by protecting your blood vessels.
Also, omega 3s have shown to reduce the triglycerides level – high levels are associated with increased risk of heart diseases.
Eating 100 to 200 gms of fatty fish, twice a week, has shown significant benefits in preventing heart diseases.
However, these positive results were coming from the natural sources of omega 3 and not from the fish oil supplements.
The picture is quite blurred when it comes to supplementary omega 3 being beneficial against heart diseases.
Unlike what the supplement companies have you believed, the omega 3 supplements have shown no particular benefits in improving your heart health.
What are the symptoms of a lack of omega 3?
A lack of omega 3 can lead to the following symptoms –
Dry, rough or dull skin
Soft or brittle nails
Brittle or lacklustre hair
Difficulty in sleeping
Excessive thirst
Suffer anxiety, depression or mood swings
Difficulty in paying attention
Poor wound healing
Increased susceptibility to infections
How long does it take for omega 3 to work?
The duration before seeing any positive effects of omega 3 in your body, depends on a lot of factors. Such as, whether omega 3 is coming from a dietary source or a supplementary source, age, target organ and, quality of the oil.
Optimum omega 3 dosages can start showing results anywhere from 1 to 3 months.
How much omega 3 should I take?
There is no set guideline for how much omega 3 you should take daily.
According to WHO (World Health Organization), an adult should take between 250 mg to 2 gm of combined EPA+DHA.
NIH (National Institutes of Health), recommends an intake of omega 3 (ALA) for an adult male should be 1.6 gm and female 1.1 gm.
EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) dietary recommendation of EPA+DHA for an adult European is between 250 to 500 mg/day.
Based on the above guidelines of these organizations, we can say 500 to 1000 mg/day of EPA+DHA and 1.1 to 1.6 gm of ALA is optimum.
I aim for 1000 mg of combined EPA+DHA.
How much omega 3 can be harmful?
A dosage up to 2 to 3 gm for omega 3 supplements are considered safe by health authorities. EFSA says 5 gm of omega 3 supplements to be safe.
But a dose higher than 5 gm of omega 3 supplements, have not shown to have any additional benefits and it increases the risk of side effects.
What are the side effects of fish oil supplements?/ What happens when you eat too much omega 3?
There are no significant side-effects of omega 3 supplements. But remember, an excess of anything is bad. High doses of fish oil supplements may manifest mild side-effects.
Can raise Blood Sugar – A study conducted on diabetic patients found that high doses (8gm/day) of fish oil taken for eight weeks can increase fasting blood sugar by 22% and after-meal glucose by 35%. The study concluded that diabetics should avoid taking large doses of fish oil.
Decreases Blood Pressure – Omega 3 is beneficial for those with high blood pressure. However, people with low blood pressure should not take high doses (5-6gm/day) of fish oil supplements.
A meta-analysis of 31 studies concludes that fish oil can significantly lower your blood pressure.
Vitamin A Toxicity – An overdose of Vitamin A causes toxicity. Omega 3 supplement Cod Liver Oil is very high in Vitamin A. Taking a tablespoon of Cod Liver Oil can give you more than 13000 IU – a very high dose – of vitamin A.
RDA (Recommended Dietary Allowance) of Vitamin A is 5000 IU.
What is the best time to take omega 3 or fish oil?
No one conducted research or a study on the timing of omega 3 or fish oil. But to avoid a common side effect – the fishy aftertaste – take it around your bedtime.
Do not take fish oil on an empty stomach as it can cause gastric distress and indigestion. Also, omega 3 has shown to improve your sleep quality.
Therefore, having fish oil with your dinner is the best time.
What is the best way to take fish oil?
For the maximum absorption of omega 3 (EPA and DHA) from fish oil supplements, always take it with a meal containing healthy fats.
The fat content in the meal will stimulate the bile and pancreatic lipase enzymes (fat-digesting enzymes). It breaks down the dietary fat in the digestive system.
The fat-digesting enzymes will enhance the absorption of the omega 3 fatty acids present in fish oil.
Studies have shown that the absorption of omega 3 fatty acids increases by 300% when taking fish oil with a high-fat meal (44gm) compared to a low-fat meal (8gm).
Is there any food you should avoid taking with it?
There are a few things that affect the proper absorption of fish oil.
Avoid taking fish oil with alcohol or wine – Having fish oil with wine (or spirit) won’t cause any ill effect, but it will reduce the absorption of nutrients from fish oil.
Avoid taking fish oil with tea or coffee – Caffeine content of tea and coffee speeds up the digestive process by increasing the peristaltic movement of the digestive tract.
Peristaltic movement refers to the forward contraction force, which pushes the food through the digestive tract.
Due to this, the omega 3 fatty acids won’t be able to stay longer in the digestive tract, reducing its absorption rate.
How to read the omega 3 supplement label?
When an omega 3 supplement claims to contain 1000 mg fish oil that doesn’t mean you are getting 1000mg of EPA+DHA.
Most supplements contain 300 mg of EPA+DHA (180 EPA and 120 DHA). So, to get 1000 mg of EPA+DHA, you would have to take 3-4 capsules.
Look for brands that contain a higher concentration of EPA and DHA.
- Serving size – Serving size means the number of capsules necessary to get the listed dose of EPA and DHA.
- Total Omega 3 – Amount of total omega-3 should be highest in each serving.
- Add EPA and DHA values – Good quality supplements should contain a higher concentration of EPA+DHA.
- Look for antioxidants – Check for vitamin E. Look for the word tocopherol – an active form of vitamin E.
Things to look for, before purchasing a fish oil supplement
Apart from reading the label, keep the following checklist in mind when looking for a good quality fish oil.
1. Amount of omega 3 – Many fish oil supplements has an insignificant amount of EPA and DHA. Make sure the supplement you choose contains an optimum amount of EPA and DHA.
The supplement may claim to contain 1000 mg fish oil. However, the back of the supplement label will disclose that in this 1000mg only 300 mg of (EPA+DHA) is present.
An informed person will never fall for this marketing tactic.
2. Authenticity and Purity – Look for a brand with a “third party test stamp” on them. The independent third party test will ensure the purity of the fish oil like mercury-free, heavy metal-free, quality of the fish used for the manufacturing, extraction process.
It will also ensure that the product contains what it claims on its label.
3. Antioxidant content – Check whether the product contains antioxidants like vitamin E or not. Antioxidants help in maintaining the purity and freshness of the fish oil.
Look for the word alpha-tocopherol – the active form of vitamin E – on the label.
4.Freshness – The omega 3s in the fish oil is prone to turn rancid and can become less effective or even harmful for health. Stale fish oil will have a foul smell to it.
Always check the manufacturing date and smell the product for any foul smell.
Which omega 3 supplements are the best?
A good quality fish oil is the best option for most people to keep a healthy level of omega 3 fatty acids in the body.
However, most 1000 mg fish oil supplements contain no more than 300 mg of EPA and DHA. The rest 70% are other types of fat.
To get a 1000 mg of EPA and DHA, you will have to consume a large amount of other fats and vitamin A.
So, look for a supplement brand that provides you with a concentrated omega 3 – 90% EPA and DHA – in one capsule.
To ensure the quality of fish oil, look for a “third party quality check” stamp on the product.
Look for brands containing omega 3 in the form of free fatty acids, phospholipids, or triglycerides.
Here are the best brands you can check out: Nordic Naturals Omega-3, OmegaVia Pharma-Grade Fish Oil, Ascenta Nutrasea
Looking for a good quality fish oil on a budget? Wow omega 3, Healthy Hey Nutrition Fish Oil, TrueBasics Ultra Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Bottom line: The best way to get the required omega 3 quantity is through natural sources. Natural sources have shown many beneficial and protective effects.
But if eating fish every day is not possible, then add a good quality fish oil supplement to your diet to get the required quantity of omega 3.
Conclusion
In a way, omega 3 is proof that we evolved from a sea creature. Omega 3 is vital for our health, and its best natural source is fatty fish. A land-bound animal won’t depend on an ocean for an essential nutrient.
I don’t recommend many supplements and focus on natural sources to get all nutrient requirements. For me, supplements of omega 3 are one of the few supplements that I advocate everyone to add in their diet.
Indian diet is predominantly a vegetarian diet, and there are no good quality vegetarian sources for omega 3. So, to get all the benefits of omega 3, supplements become a compulsory addition to our diet.
Take my example, I cannot eat fish every day so fish oil becomes an essential and a convenient option to get my daily dose of omega 3.
Use this guide as a reference when you purchase an omega 3 supplement and share it with your friends who want to buy it.
If you have any other questions regarding omega 3, feel free to ask the questions in the comment below.
Articles You May like
7 Amazing Benefits Of Vitamin D That Will Boost Your Immunity
21 Immunity Boosting Foods With Hidden Ayurvedic Benefits
Leave a Reply